Slot Harmonics Means
Equipment that generate harmonics In industrial applications, the main types of equipment that generate harmonics are: static converters, arc furnaces, lighting, saturated reactors and other equipment, such as rotating machines which generate slot harmonics (often negligible). Two wide rectangle-shaped microstrip-fed 2.6-GHz slot antennas using defected ground structures (DGSs) with a low design complexity are proposed to achieve wideband harmonic suppression. To accomplish this, two rectangular DGSs (RDGSs) in the first antenna and two circular DGSs (CDGSs) in the second one with various dimensions are etched into the ground plane, which could have a wideband-stop. Harmonics are generally classified by their name and frequency, for example, a 2 nd harmonic of the fundamental frequency at 100 Hz, and also by their sequence. Harmonic sequence refers to the phasor rotation of the harmonic voltages and currents with respect to the fundamental waveform in a balanced, 3-phase 4-wire system.
Behaviors of the slot harmonics under distorted air-gap flux waveform. The third-harmonic air-gap flux is intentionally injected into an induction motor to distort the flux waveform. The slot harmonics from the rotor are measured with or without the load under various air.
Holes and cylinders are the most commonly produced forms in the modern machine shop. Usually, the diameter is the critical dimension to be measured, but when a part needs to interact with other parts, form and surface finish must also be taken into account.

Read Next
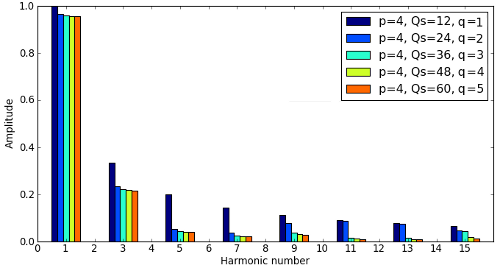
This Harmonic Analysis chart shows a range of harmonics and their amplitude.
Holes and cylinders are the most commonly produced forms in the modern machine shop. Usually, the diameter is the critical dimension to be measured, but when a part needs to interact with other parts, form and surface finish must also be taken into account. When the diameter is tight, form error can take up a significant part of the tolerance.
There are many standards that describe how form measurements are to be made. Diametral (two-point diameter) and chordal (vee block) are probably the must common standards, although they provide the least amount of real information. Form measurements such as roundness are best done with a radial method, usually using a form gage.
Form errors are a blueprint of the machining process—the cutting tool, the machine and the environment all leave their marks on the machined part. Embedded within the roundness of the part are a series of lobes which can have a large impact on how the part performs, especially when the part rotates at very high speeds.
In addition to roundness analysis, quality engineers use harmonic analysis tools to predict what a part might do under certain conditions. By decomposing the out-of-roundness trace into a collection of sinusoidal components, called harmonics, harmonic analyses can provide information about the dominant lobes found within the part.
By using harmonic analysis you can figure out what creates the lobing conditions on the part. There are three major contributors to the lobing condition.
Slot Harmonics Means Meaning
The first harmonic is called the fundamental sinusoid. Its wavelength is the entire length of the circumference (over 360 degrees) and it measures geometry errors that repeat once per revolution. These errors tend to be the result of an eccentric error, such as placing the part off-center when it is first set up in the machine.
The second harmonic measures errors that repeat twice per revolution, so its wavelength is one half the fundamental wavelength (over 180 degrees). Second harmonic problems are often the result of an out-of-squareness condition in the machine tool, the fixture or the measurement setup.
The third harmonic measures errors that repeat three times per revolution. Its wavelength is one third of the fundamental wavelength (over 120 degrees). In the same vein, the Nth harmonic, then, is a sinusoid whose wavelength is the fundamental wavelength divided by N. Third and higher harmonics problems are often the result of workpiece clamping, a particular aspect of the manufacturing process or various sources of vibration. For example, a three-point chuck is apt to produce an odd number of lobes.
Slot Harmonics Means Test
In the bearing industry, performance (lack of noise and vibration) is related to the presence and magnitude of certain lobes (harmonics).
An interesting example is the case of a marine engine manufacturer who suddenly encountered a peculiar noise from one of the bearings being supplied by its bearing supplier. The company checked records and found that testing was being done to inspect as many as 50 lobes per revolution.
However, dynamic analysis on the engine revealed that the vibration or noise had a period of roughly 120 cycles per revolution. The harmonic analysis was expanded to look for shorter wavelength errors and confirmed the presence of a 120-lobed condition. The cause was eventually tracked to some unrelated changes on the shop floor. The changes had triggered a slight increase in vibration that was just enough to cause the problem for the engine builder.
Slot Harmonics Define
With the form equipment available today, harmonic analysis is as easy as setting up some test parameters. However, the results can be invaluable in producing better parts and better performing machines.